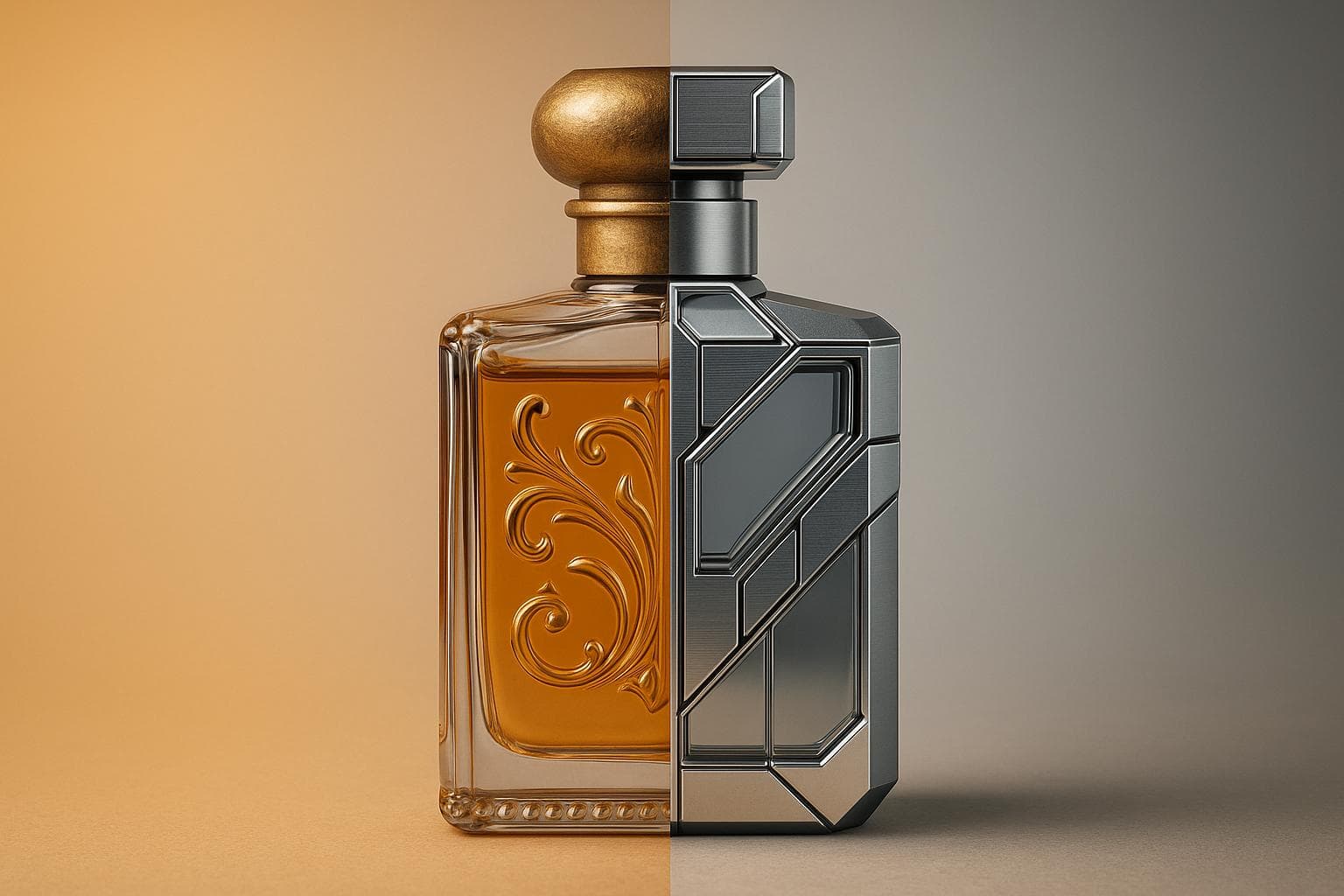
Η τεχνητή νοημοσύνη (AI) αλλάζει τον κόσμο των αρωμάτων, επιταχύνοντας διαδικασίες που παλαιότερα διαρκούσαν χρόνια. Ενώ οι "μύτες" (master perfumers) στηρίζονται σε χρόνια εκπαίδευσης και μνήμης για να δημιουργήσουν αρώματα, η AI χρησιμοποιεί δεδομένα και αλγορίθμους για να προτείνει συνθέσεις μέσα σε λίγες ώρες. Δείτε συνοπτικά πώς συγκρίνονται αυτές οι δύο μέθοδοι:
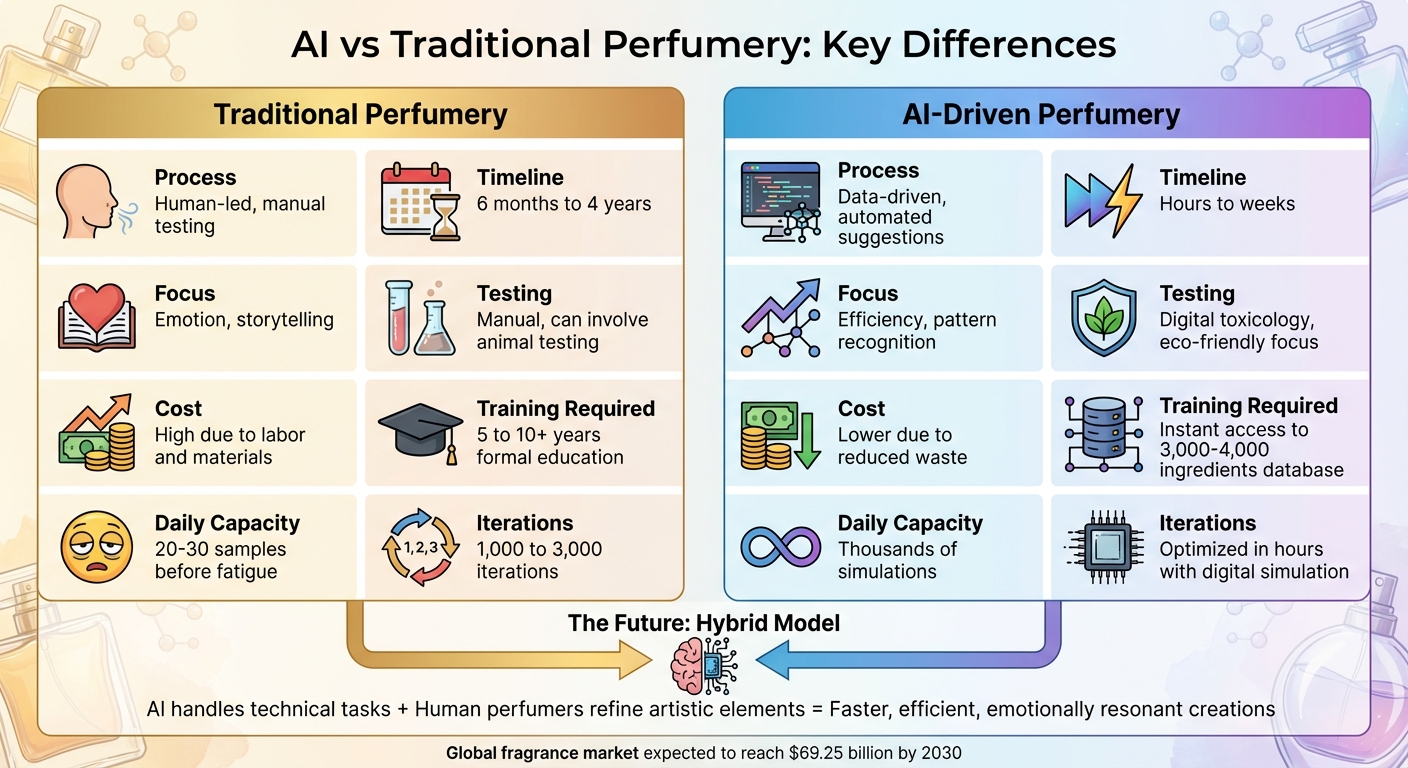
- Παραδοσιακή Αρωματοποιία: Βασίζεται στην ανθρώπινη δεξιοτεχνία, διαίσθηση και αφήγηση. Τα αρώματα δημιουργούνται σε διάστημα μηνών ή ετών, με χιλιάδες δοκιμές συστατικών.
- Αρωματοποιία με Τεχνητή Νοημοσύνη: Χρησιμοποιεί machine learning για ανάλυση βάσεων δεδομένων συστατικών, καταναλωτικών προτιμήσεων και στοιχείων ασφάλειας. Μπορεί να παράγει συνταγές σε λίγες ημέρες, μειώνοντας σπατάλη και χρόνο ανάπτυξης.
Και οι δύο προσεγγίσεις έχουν τα πλεονεκτήματά τους: οι μεθόδοι με ανθρώπινη καθοδήγηση δίνουν προτεραιότητα στην τέχνη και το συναίσθημα, ενώ η AI προσφέρει ταχύτητα, ακρίβεια και καινοτομία. Όλο και περισσότερες μάρκες συνδυάζουν και τα δύο για πιο γρήγορες, αποδοτικές αλλά και συναισθηματικά φορτισμένες δημιουργίες.
Γρήγορη Σύγκριση:
| Πτυχή | Παραδοσιακή Αρωματοποιία | Αρωματοποιία με AI |
|---|---|---|
| Διαδικασία | Ανθρώπινη καθοδήγηση, χειροκίνητες δοκιμές | Αυτοματοποιημένες, βάσει δεδομένων προτάσεις |
| Χρονοδιάγραμμα | 6 μήνες έως 4 χρόνια | Ώρες έως εβδομάδες |
| Εστίαση | Συναίσθημα, αφήγηση | Αποδοτικότητα, αναγνώριση προτύπων |
| Δοκιμές | Χειροκίνητες, μπορεί να περιλαμβάνουν δοκιμές σε ζώα | Ψηφιακή τοξικολογία, οικολογική εστίαση |
| Κόστος | Υψηλό λόγω εργασίας & υλικών | Χαμηλότερο λόγω ελαχιστοποίησης απωλειών |
Η εξέλιξη αυτή διαμορφώνει ένα υβριδικό μοντέλο όπου η AI διαχειρίζεται τεχνικές εργασίες και οι αρωματοποιοί εξευγενίζουν τις καλλιτεχνικές πτυχές. Είτε σας ελκύει η δεξιοτεχνία των παραδοσιακών μεθόδων είτε η αποτελεσματικότητα της AI, το μέλλον της αρωματοποιίας παντρεύει ιδανικά και τους δύο κόσμους.
AI vs Παραδοσιακή Αρωματοποιία: Σύγκριση Πλευρά με Πλευρά
Πώς Λειτουργεί η Παραδοσιακή Αρωματοποιία
Ο Ρόλος του Αρωματοποιού
Οι παραδοσιακοί αρωματοποιοί, που συχνά αποκαλούνται "μύτες", αφιερώνουν 5 έως 10+ χρόνια σε επίσημη εκπαίδευση και πρακτική άσκηση πριν δημιουργήσουν μοναδικά δικά τους αρώματα. Σε αυτό το διάστημα, ακονίζουν την όσφρησή τους και απομνημονεύουν τα χαρακτηριστικά περισσοτέρων από 1.000 συστατικά από μια παλέτα 3.000 έως 4.000 πρώτων υλών. Αυτή η διαδικασία θυμίζει τους σεφ ή τους sommeliers που χτίζουν βαθιά γνώση στις γεύσεις. Οι master perfumers μαθαίνουν να ξεχωρίζουν κάθε συστατικό σε διάφορες αραιώσεις και απειράριθμους συνδυασμούς.
Η δουλειά τους είναι ένα πάντρεμα τέχνης και επιστήμης. Μεταφράζουν αφηρημένες έννοιες – όπως διαθέσεις, τόπους ή και συναισθήματα – σε προσεκτικά δημιουργημένες οσμές. Για παράδειγμα, ένα brief που περιγράφει "μια ταράτσα της Νέας Υόρκης το καλοκαίρι" μπορεί να δώσει έμπνευση για μια κιτρώδη-αρωματική σύνθεση, ενώ μια έννοια "αισθησιακής" θηλυκότητας μπορεί να καταλήξει σε ένα λουλουδένιο-ξυλώδες musk. Πέρα από τη δημιουργικότητα, ο αρωματοποιός διαχειρίζεται και πρακτικές προκλήσεις, όπως κανονισμούς, προϋπολογισμό και προμήθεια πρώτων υλών. Ισορροπούν αριστοτεχνικά σπάνιες και ακριβές φυσικές ύλες όπως τριαντάφυλλο ή γιασεμί με αξιόπιστα συνθετικά όπως hedione ή Iso E Super. Αυτή η εμπειρία είναι κεντρική στην επαναληπτική διαδικασία δημιουργίας ενός αρώματος.
Η Διαδικασία Ανάπτυξης
Αφού ερμηνεύσει το brief, ο αρωματοποιός συντάσσει μία ή περισσότερες δοκιμαστικές φόρμουλες που προετοιμάζει το εργαστήριο. Η αρχική φόρμουλα αποτελεί βάση για περαιτέρω βελτίωση. Οι αρωματοποιοί αξιολογούν – σε blotters και δέρμα – πώς εξελίσσεται ένα άρωμα από τις κορυφαίες στις μεσαίες και στις νότες βάσης, ελέγχουν τη συμβατότητα και τη σταθερότητα. Ωστόσο, η ανθρώπινη όσφρηση έχει όρια· μπορεί να αξιολογήσει μόνο 20–30 δείγματα την ημέρα πριν επέλθει κόπωση.
Η δημιουργία του τέλειου αρώματος απαιτεί αμέτρητες ρυθμίσεις για την επίτευξη της ισορροπίας λάμψης, γλυκύτητας, διάχυσης και διάρκειας, διατηρώντας πάντα τον επιθυμητό χαρακτήρα. Συχνά συμμετέχουν panels καταναλωτών που δίνουν feedback για χαρακτηριστικά όπως απήχηση, ποιότητα και προσδοκία αγοράς. Αυτή η συμβολή μπορεί να οδηγήσει σε σημαντικές αλλαγές. Η συνολική διαδικασία, από την ιδέα έως την ολοκλήρωση, μπορεί να διαρκέσει από 6 μήνες έως 4 χρόνια, ενώ κάποιες φόρμουλες υπερβαίνουν τις 1.000–3.000 δοκιμές μέχρι να τελειοποιηθούν. Η σχολαστική αυτή προσέγγιση χαρίζει βάθος και πολυπλοκότητα αλλά περιορίζει εκ φύσεως τον ρυθμό ανάπτυξης νέων αρωμάτων.
Δυνατά Σημεία και Περιορισμοί
Η παραδοσιακή αρωματοποιία διαπρέπει όταν η διαίσθηση, η εμπειρία και η αφήγηση είναι καθοριστικές. Οι αρωματοποιοί ενσωματώνουν στις δημιουργίες τους προσωπικές μνήμες, πολιτιστικές επιρροές και αφηγήματα, μεταμορφώνοντας έναν κήπο των παιδικών χρόνων ή έναν φανταστικό χαρακτήρα σε μελετημένα συστατικά και συμφωνίες. Οι μοναδικές τους οπτικές και η καλλιτεχνική διαίσθηση οδηγούν σε αρώματα που προκαλούν έντονα συναισθήματα ή πρωτοπορούν, συχνά έξω από τις τάσεις.
Αυτή η μέθοδος όμως είναι ιδιαίτερα χρονοβόρα και δαπανηρή, απαιτώντας τη συνεργασία αρωματοποιών, εργαστηριακών, αξιολογητών, marketing και κανονιστικών ομάδων για μήνες ή και χρόνια. Κάθε γύρος αναθεώρησης καταναλώνει πολύτιμες πρώτες ύλες και εργαστηριακούς πόρους, ενώ οι καταναλωτικές δοκιμές αυξάνουν σημαντικά το κόστος. Όλοι αυτοί οι παράγοντες κάνουν την παραδοσιακή αρωματοποιία ακριβή υπόθεση και περιορίζουν τη δυνατότητα κλιμάκωσης. Οι αυστηρές προθεσμίες ενδέχεται να επηρεάσουν την ποιότητα και οι παρατεταμένοι χρόνοι ανάπτυξης αυξάνουν τον κίνδυνο – όπως αλλαγές τάσεων ή ακυρώσεις αν τα tests δεν ανταποκριθούν στις προσδοκίες. Για τους Αμερικανούς καταναλωτές, αυτές οι προκλήσεις αποτυπώνονται στην υψηλή τιμή των luxury αρωμάτων, που συχνά ξεπερνούν τα $200–$300 ανά φιάλη. Ωστόσο, πολλοί αγοραστές δεν χρησιμοποιούν ποτέ ολόκληρη τη φιάλη τους, υπογραμμίζοντας την αναποτελεσματικότητα του μοντέλου.
Εδώ έρχονται οι δοκιμαστικές φιάλες της Scento (0.75ml, 2ml, 8ml) και οι συνδρομητικές επιλογές, προσφέροντας έναν προσιτό τρόπο δοκιμής πολυτελών αρωμάτων χωρίς τη δέσμευση της αγοράς ολόκληρου μπουκαλιού. Αυτά τα μικρότερα μεγέθη διευκολύνουν την ανακάλυψη και απόλαυση υψηλής ποιότητας αρωμάτων, παρακάμπτοντας το υψηλό κόστος της παραδοσιακής προσέγγισης.
Πώς Λειτουργεί η Αρωματοποιία με AI
Εργαλεία & Τεχνολογίες AI
Η AI μεταμορφώνει τη δημιουργία αρωμάτων αξιοποιώντας machine learning και ψηφιακά εργαστήρια χημείας. Τα εργαλεία αυτά εκπαιδεύονται σε τεράστια δεδομένα, όπως υπάρχουσες φόρμουλες, ιδιότητες συστατικών, τοξικολογικά και καταναλωτικές προτιμήσεις. Ένα τέτοιο εργαλείο, το Symrise Philyra, που αναπτύχθηκε με τη IBM, αναλύει χιλιάδες φόρμουλες και πρώτες ύλες για να προτείνει νέους συνδυασμούς. Αυτές οι προτάσεις βελτιστοποιούνται τόσο σε δημιουργικότητα όσο και σε στόχους κοινού και αποδοτικότητα κόστους.
Ένα ακόμη κορυφαίο εργαλείο είναι το Givaudan Carto, που επιτρέπει στους αρωματοποιούς να αλληλεπιδρούν με οθόνη αφής. Ο αρωματοποιός επιλέγει πρώτες ύλες και ένα ρομπότ παράγει άμεσα δείγματα με μόλις 10 ml ανά κύκλο. Το σύστημα παράγει επίσης "Χάρτη Οσφρητικής Αξίας", αναδεικνύοντας τη συνεισφορά κάθε συστατικού. Έτσι διασφαλίζεται άριστη οσφρητική απόδοση με τήρηση κανονισμών ασφαλείας. Εν τω μεταξύ, το ChemcoPilot πηγαίνει ακόμα πιο πέρα, προσομοιώνοντας την απόδοση του αρώματος στο δέρμα, προβλέποντας τοξικολογικούς κινδύνους και υπολογίζοντας περιβαλλοντικούς παράγοντες όπως τις εκπομπές CO₂ πριν την οποιαδήποτε φυσική δοκιμή. Εταιρείες όπως η Grupo Boticário και η Natura &Co στη Βραζιλία βασίζονται σε τέτοιες πλατφόρμες για τη δημιουργία ασφαλέστερων και φιλικότερων προς το περιβάλλον αρωμάτων χωρίς δοκιμές σε ζώα. Αυτά τα προηγμένα εργαλεία αποτελούν τον πυρήνα της βελτιστοποιημένης εργασίας με AI, που εξετάζουμε στη συνέχεια.
Η Ροή Εργασίας της AI στην Αρωματοποιία
Το ταξίδι ξεκινά με ένα ολοκληρωμένο brief και εισαγωγή δεδομένων. Οι ομάδες εισάγουν λεπτομέρειες για το κοινό-στόχο, τις τάσεις της αγοράς, τα επιθυμητά προφίλ αρωμάτων, κανονιστικές απαιτήσεις, περιορισμούς προϋπολογισμού και στόχους βιωσιμότητας. Το σύστημα AI στη συνέχεια αναλύει τα δεδομένα, εντοπίζοντας πρότυπα και συσχετίσεις ανάμεσα σε μοριακές δομές, οσφρητικούς όρους και ανθρώπινες αντιδράσεις. Έτσι εντοπίζει υποσχόμενους συνδυασμούς υλικών.
Στη συνέχεια, η AI παράγει υποψήφιες φόρμουλες, προτείνοντας λίστες συστατικών και δοσολογίες που ευθυγραμμίζονται με το brief εξασφαλίζοντας πάντα ασφάλεια, κόστος και κανονιστικά όρια. Ψηφιακές ενότητες αξιολογούν αυτές τις φόρμουλες ως προς απόδοση και ασφάλεια, εξετάζοντας πτητικότητα, διάρκεια, συμβατότητα με το δέρμα, τοξικότητα και περιβαλλοντική επίπτωση – όλα πριν ξεκινήσει εργαστηριακή εργασία. Αρωματοποιοί ή αξιολογητές επανεξετάζουν τις επικρατέστερες προτάσεις και τα αποτελέσματα οδηγούν σε επαναληπτικές βελτιώσεις. Αυτή η διαδικασία μειώνει θεαματικά τον χρόνο ανάπτυξης, που παραδοσιακά κυμαινόταν από έξι μήνες έως αρκετά χρόνια, σε μόλις εβδομάδες ή μήνες.
Πλεονεκτήματα και Περιορισμοί
Η αρωματοποιία με AI προσφέρει πολλαπλά οφέλη αλλά και ορισμένες προκλήσεις. Προσομοιώνοντας αποτελέσματα και φιλτράροντας επιλογές ψηφιακά, η AI μειώνει την ανάγκη για μαζικές εργαστηριακές δοκιμές. Έτσι περιορίζεται η κατανάλωση πρώτων υλών, εξοικονομείται εργαστηριακός χρόνος και μειώνεται το κόστος εργασίας. Ψηφιακές πλατφόρμες χημείας συμβάλλουν και στη μείωση οικολογικού αποτυπώματος, σπατάλης και επικίνδυνων παραπροϊόντων, επιλέγοντας eco-friendly μόρια και βελτιστοποιώντας τις μεθόδους σύνθεσης. Η προγνωστική τοξικολογία απλοποιεί περαιτέρω τη διαδικασία μειώνοντας την ανάγκη για εκτεταμένες φυσικές δοκιμές ασφάλειας και απρόσμενες αναδιαμορφώσεις.
Η AI της L’Oréal για παράδειγμα, επιτυγχάνει 95% ακρίβεια στην ανακάλυψη αρωμάτων για τους πελάτες, αποκαλύπτοντας τις δυνατότητες των συστημάτων αυτών. Παράλληλα, η παγκόσμια αγορά αρωμάτων προβλέπεται να φθάσει τα $69,25 δισ. έως το 2030. Η AI υποστηρίζει μαζική εξατομίκευση αναλύοντας δεδομένα όπως προτιμήσεις, κριτικές, ιστορικό αγορών και δημογραφικά στοιχεία. Αυτό επιτρέπει στις μάρκες να εντοπίζουν πρότυπα – π.χ. προτίμηση σε δροσερά κιτρώδη ή γλυκά gourmand – και να διαμορφώνουν συνταγές κομμένες στα μέτρα συγκεκριμένων ομάδων καταναλωτών. Πλατφόρμες όπως το Scento αξιοποιούν αυτές τις γνώσεις για εξατομικευμένες προτάσεις.
Ωστόσο, η αποτελεσματικότητα της AI εξαρτάται έντονα από την ποιότητα των εκπαιδευτικών της δεδομένων. Εάν τα datasets εμπεριέχουν μεροληψίες ή ελλείψεις – π.χ. έμφαση σε συγκεκριμένες χημείες ή αγορές – οι συστάσεις μπορεί να γίνουν επαναλαμβανόμενες ή να παραβλέψουν κρίσιμες παραμέτρους ασφάλειας. Επίσης, η προσκόλληση σε ιστορικές επιτυχίες μπορεί να οδηγήσει σε συνταγές που ακολουθούν τη μόδα αντί της καινοτομίας. Από καλλιτεχνική σκοπιά, κάποιοι αρωματοποιοί θεωρούν πως η AI δεν μπορεί να αναπαράγει τα ενστικτώδη άλματα, τη συναισθηματική αφήγηση και το “σπάσιμο κανόνων” που προσδίδουν ψυχή στην αρωματοποιία. Υπάρχει επίσης ο κίνδυνος υπερβολικής αξιοποίησης του “μαύρου κουτιού”, όπου οι συνθέσεις γίνονται δεκτές χωρίς ενδελεχή ανθρώπινο έλεγχο ως προς ασφάλεια, δεοντολογία ή δημιουργικό όραμα. Αυτοί οι παράγοντες καταδεικνύουν τη διαρκή ισορροπία μεταξύ τεχνολογικής αποδοτικότητας και ανθρώπινης τέχνης στη σύγχρονη αρωματοποιία.
Βασικές Διαφορές μεταξύ AI και Παραδοσιακής Αρωματοποιίας
Δημιουργική Διαδικασία & Συγγραφή
Η παραδοσιακή αρωματοποιία έχει βαθιές ρίζες στην ανθρώπινη δημιουργικότητα και διαίσθηση. Οι master perfumers – οι περίφημες "μύτες" – στηρίζονται σε χρόνια εμπειρίας και προσωπικής μνήμης για να δημιουργήσουν αρώματα που αποδίδουν συναίσθημα και αφήγηση. Κάθε άρωμα κουβαλά μία ξεχωριστή ταυτότητα, διαμορφωμένη από τη μοναδική καλλιτεχνική οπτική του δημιουργού του.
Με την έλευση της AI, αλλάζει άρδην η προσέγγιση. Αντί να βασίζεται εξ ολοκλήρου στη διαίσθηση, η AI επεξεργάζεται τεράστιες ποσότητες δεδομένων, από μοριακές δομές και ιδιότητες υλικών έως ιστορικές φόρμουλες, προτείνοντας συνδυασμούς που ίσως ο άνθρωπος δεν θα φανταζόταν. Ωστόσο, η AI δεν αντικαθιστά τη δημιουργικότητα – λειτουργεί ως εργαλείο ενίσχυσης της. Ένα χαρακτηριστικό παράδειγμα είναι ο Loc Dong της IFF που χρησιμοποίησε AI για να ενισχύσει τη δοσολογία του styrallyl acetate και να το συνδυάσει με accord λαβάντας, οδηγώντας σε πρωτοποριακό άρωμα. Αυτή η συνεργασία ελάφρυνε το φόρτο δουλειάς διατηρώντας όμως την καλλιτεχνική ακεραιότητα της διαδικασίας. Η AI διευκολύνει την επιλογή υλικών και τη βελτιστοποίηση συνταγών δίνοντας νέα διάσταση στη δημιουργία αρωμάτων.
Ταχύτητα και Αποδοτικότητα
Η παραδοσιακή διαδικασία δημιουργίας αρωμάτων απαιτεί χρόνο – από έξι μήνες έως τέσσερα χρόνια. Το χρονοβόρο αυτό αποτέλεσμα οφείλεται στις πολυάριθμες επαναλήψεις και διορθώσεις που απαιτούνται έως το ιδανικό αποτέλεσμα.
Η AI, αντιθέτως, μειώνει δραματικά αυτούς τους χρόνους. Σε ορισμένες περιπτώσεις, εργασίες που διαρκούσαν μήνες υλοποιούνται σε ώρες ή μέρες. Για παράδειγμα, η ολλανδική startup EveryHuman χρησιμοποιεί αλγορίθμους και ερωτηματολόγια για τη δημιουργία μοναδικών αρωμάτων σε λίγα λεπτά. Αντίστοιχα, το 2019, η Symrise και η IBM μέσω της AI Philyra ανέπτυξαν πολλαπλές εκδοχές για τη συλλογή του O Boticário για την Ημέρα του Αγίου Βαλεντίνου. Αξιοσημείωτα, τα τυφλά tests προτίμησαν άρωμα που δημιουργήθηκε αποκλειστικά από AI.
Περιβαλλοντική Επίδραση & Ασφάλεια
Η παραδοσιακή αρωματοποιία περιλαμβάνει συχνά εκτεταμένες χειροκίνητες δοκιμές, που παράγουν σημαντικά απόβλητα και κάποιες φορές δοκιμές σε ζώα για λόγους ασφάλειας. Αυτή η προσέγγιση, ενώ αποτελεσματική, εγείρει ηθικές και περιβαλλοντικές ανησυχίες.
Η AI προσφέρει μια περισσότερο βιώσιμη εναλλακτική. Εργαλεία όπως το Chemcopilot μπορούν να προβλέψουν πώς αντιδρά ένα άρωμα στο δέρμα, να υπολογίσουν το αποτύπωμα άνθρακα και να εντοπίσουν eco-friendly μόρια – όλα πριν καμία εργαστηριακή δοκιμή. Εταιρείες όπως Grupo Boticário και Natura &Co αξιοποιούν AI για τη δημιουργία «cruelty-free» αρωμάτων, μειώνοντας τη σπατάλη, ελαχιστοποιώντας εκπομπές άνθρακα και αντιμετωπίζοντας τις ηθικές προκλήσεις κατά πρόσωπο.
Χρήση Δεδομένων & Ανατροφοδότηση
Οι μηχανισμοί feedback διαφέρουν επίσης δραστικά. Οι παραδοσιακές μέθοδοι στηρίζονται κυρίως σε μικρής κλίμακας ποιοτική αξιολόγηση από panels ειδικών ή καταναλωτών.
Αντίθετα, η AI αξιοποιεί τεράστιες βάσεις δεδομένων, συμπεριλαμβάνοντας κριτικές καταναλωτών, ιστορικά αγορών, μοριακές συνθέσεις και αισθητηριακά feedback. Αυτό επιτρέπει βαθύτερη ανάλυση τάσεων και προτιμήσεων. Η τεχνολογία AI της L’Oréal, για παράδειγμα, επιτυγχάνει 95% ακρίβεια στη σύσταση κατάλληλων αρωμάτων σε πελάτες. Η ανάλυση δεδομένων συνδυασμένη με εξατομίκευση επιτρέπει customization σε κλίμακα που οι παραδοσιακές μέθοδοι δεν μπορούν να φτάσουν.
Συγκριτικός Πίνακας
Ο παρακάτω πίνακας αναδεικνύει τις βασικές διαφορές μεταξύ παραδοσιακής και τεχνολογικά καθοδηγούμενης αρωματοποιίας:
| Πτυχή | Παραδοσιακή Αρωματοποιία | Αρωματοποιία με AI |
|---|---|---|
| Δημιουργική Διαδικασία | Ανθρώπινη δημιουργικότητα και αφήγηση | Προτάσεις βάσει δεδομένων και νέα ζεύγη |
| Ταχύτητα | 6 μήνες–4 χρόνια | Ώρες έως μέρες με χρήση προσομοιώσεων & ρομποτικής |
| Περιβάλλον/Ασφάλεια | Χειροκίνητες δοκιμές, πιθανή χρήση ζώων & σπατάλη | Ψηφιακές προγνώσεις τοξικολογίας, χαμηλότερο CO₂, πράσινα μόρια |
| Δεδομένα/Ανατροφοδότηση | Μικρής κλίμακας panels ειδικών | Τεράστια datasets, real-time ανάλυση τάσεων και βελτιστοποίηση |
Όπου Συναντώνται Η Εξειδίκευση και οι Αλγόριθμοι
Το Υβριδικό Μοντέλο
Στη σύγχρονη βιομηχανία αρωμάτων, η τεχνητή νοημοσύνη (AI) και η ανθρώπινη δημιουργικότητα συνεργάζονται αρμονικά. Η AI μπορεί να εξερευνά τεράστιες βάσεις υλικών, να σχεδιάζει αρχικές φόρμουλες και να προβλέπει τις επιδόσεις τους. Όμως το μαγικό στοιχείο προσθέτουν οι αρωματοποιοί – αξιολογώντας αρώματα σε blotters και δέρμα, διορθώνοντας τις ισορροπίες υλικών και υφαίνοντας συναισθηματικές ιστορίες όπως «λινοσκεπάσματα λουσμένα στον ήλιο» για να χαρίσουν ψυχή και αφήγηση στο αποτέλεσμα.
Τα συστήματα AI, όπως συζητήθηκε, μπορούν να αναλύσουν χιλιάδες υλικά, να προβλέψουν προφίλ αρωμάτων και να προσομοιώσουν τη σταθερότητα φόρμουλας. Ωστόσο, οι ειδικοί είναι απαραίτητοι. Καθορίζουν το δημιουργικό όραμα, αξιολογούν την εξέλιξη στο δέρμα και εξασφαλίζουν πως κάθε μίγμα είναι αυθεντικό και ευθυγραμμισμένο με την ταυτότητα της μάρκας. Διαμορφώνουν το συνολικό αφήγημα – το άρωμα, την ονομασία, το μπουκάλι και το concept marketing.
Το 2019, η AI Philyra της IBM Research και της Symrise σχεδίασε φόρμουλες για συλλογή της O Boticário. Η καταναλωτική δοκιμή προτίμησε μάλιστα την 100% AI-δημιουργημένη εκδοχή. Αντίστοιχα, στην IFF η AI υποστήριξε τον αρωματοποιό Loc Dong να δημιουργήσει μελλοντικό αρωματικό προφίλ με υψηλές δόσεις styrallyl acetate και cream-lavender accord.
Το σύστημα CARTO της Givaudan είναι άλλο παράδειγμα, χρησιμοποιώντας Χάρτη Οσφρητικής Αξίας για τη βελτιστοποίηση συνθέσεων στη φάση της τελικής τελειοποίησης. Τέτοια παραδείγματα δείχνουν πώς η AI διευρύνει τις δημιουργικές δυνατότητες παραμένοντας η τελική καλλιτεχνική ευθύνη στα χέρια των ανθρώπων. Η νέα αυτή συνεργασία επαναπροσδιορίζει το ρόλο των μοντέρνων αρωματοποιών, συνδυάζοντας τεχνολογία και τέχνη.
Μεταβολές στο Ρόλο του Αρωματοποιού
Παραδοσιακά, οι αρωματοποιοί περνούσαν εβδομάδες διορθώνοντας φόρμουλες, αλλάζοντας ένα-δύο υλικά τη φορά και περιμένοντας τα αποτελέσματα πριν επαναξιολογήσουν. Η AI απλούστευσε δραστικά τη διαδικασία προσομοιώνοντας αμέτρητες παραλλαγές ψηφιακά, έτσι ώστε μόνο οι πιο ελπιδοφόρες να περνούν στη φυσική δοκιμή. Αυτή η αποδοτικότητα επιτρέπει στους αρωματοποιούς να αφιερώνουν περισσότερο χρόνο στις δημιουργικές και συναισθηματικές πτυχές του έργου τους.
Έτσι ο ρόλος του αρωματοποιού εξελίσσεται. Λειτουργούν ως δημιουργικοί διευθυντές – συντάσσοντας ολοκληρωμένα olfactory briefs, επιλέγοντας από AI-προτάσεις, ρυθμίζοντας συναισθηματικές αποχρώσεις και εξασφαλίζοντας πως η ταχύτητα δεν θυσιάζει την ποιότητα ή την ταυτότητα της μάρκας. Η διεπιστημονική συνεργασία ενισχύεται, με αρωματοποιούς, data scientists και ομάδες βιωσιμότητας να εργάζονται από κοινού. Τα εργαλεία AI εντοπίζουν κινδύνους συμμόρφωσης, υπολογίζουν CO₂ και αναλύουν τις τάσεις, βοηθώντας έτσι τις ομάδες να λαμβάνουν τεκμηριωμένες αποφάσεις.
Απαιτούνται και νέες δεξιότητες. Οι αρωματοποιοί οφείλουν να είναι εξοικειωμένοι με δεδομένα και εργαλεία AI, να κατανοούν τη λειτουργία των recommendation engines, να εντοπίζουν bias και να αποφεύγουν υπερβολικά «στρατιωτικές» συνταγές. Μαθαίνουν να διαβάζουν dashboards, να προσαρμόζουν παραμέτρους και να αξιολογούν προβλεπόμενα outputs όπως διάρκεια ή προτιμήσεις πελατών. Παράλληλα, οι soft skills – όπως η διατύπωση δημιουργικών προθέσεων, η επιμέλεια των AI επιλογών και η υπεράσπιση των καλλιτεχνικών επιλογών – είναι περισσότερο πολύτιμες από ποτέ. Οι αλλαγές αυτές επαναπροσδιορίζουν τη δημιουργική διαδικασία και ανοίγουν τον δρόμο για εξατομικευμένες καινοτομίες αρωμάτων.
Μελλοντικές Κατευθύνσεις
Κοιτάζοντας μπροστά, η AI αναμένεται να καθορίσει τη μαζική εξατομίκευση και τον βιώσιμο σχεδιασμό στον χώρο του αρώματος. Οι αλγόριθμοι μπορούν να αναλύσουν ερωτηματολόγια, αγοραστική ιστορία και δεδομένα τρόπου ζωής για να προβλέψουν ποιες νότες ταιριάζουν σε κάθε άτομο και ακολούθως να προτείνουν φόρμουλες με modular components. Οι αρωματοποιοί εξασφαλίζουν πως τα modular accords συνδυάζονται αριστοτεχνικά, διατηρούν brand identity και πληρούν τα standards ασφάλειας.
Η AI προωθεί επίσης τον οικολογικό σχεδιασμό. Μοντέλα machine learning εκπαιδευμένα σε τοξικολογικά δεδομένα και περιβαλλοντικές μετρήσεις επισημαίνουν επικίνδυνα συστατικά, υπολογίζουν εκπομπές CO₂ και προτείνουν πράσινες εναλλακτικές που διατηρούν το επιθυμητό άρωμα. Ενώ η AI εντοπίζει υποψήφιες αλλαγές, το πόσο θα διαφοροποιηθεί η συνταγή χωρίς να χάσει την καλλιτεχνική της ταυτότητα αποτελεί ευθύνη του αρωματοποιού.
Σε κάποιες περιπτώσεις, η AI δημιουργεί ακόμη και απευθείας νέα μόρια οσμής. Αναλύοντας τεράστιες databases υφιστάμενων odorants, τα συστήματα προτείνουν καινοτόμα μόρια – όπως ξυλώδεις-amber νότες με χαμηλό αλλεργικό ρίσκο – σταθερά, παραγωγικά και eco-friendly. Οι χημικοί παράγουν τα υποσχόμενα μορια, και οι αρωματοποιοί τα αξιολογούν, συχνά εντοπίζοντας λεπτές αποχρώσεις που απογειώνουν το άρωμα. Αυτό το feedback βελτιώνει περαιτέρω τα predictive μοντέλα της AI.
Για τους καταναλωτές, η υβριδική αυτή προσέγγιση σημαίνει περισσότερες εξατομικευμένες επιλογές και ευκολότερη ανακάλυψη νέων αγαπημένων. Πλατφόρμες με δοκιμαστικά ή travel-size μπουκάλια μπορούν να προσφέρουν AI προτάσεις βάσει ατομικών προτιμήσεων, ενώ οι ειδικοί συνεχίζουν να επιμελούνται και να αφηγούνται τις συλλογές. Υπηρεσίες όπως το Scento, που διαθέτει designer και niche αρώματα σε decants (0.75 ml, 2 ml, 8 ml), μπορούν να συνδυάσουν AI προτάσεις με την ανθρώπινη αφήγηση. Αυτό είναι ιδιαίτερα πολύτιμο σε μία αγορά που από περίπου 300 releases ετησίως τη δεκαετία του ’90 φτάνει πλέον τα 3.000+ σήμερα.
sbb-itb-fb213bc
Τι Σημαίνει Αυτή η Εξέλιξη για τους Αγοραστές Αρωμάτων
Ανακάλυψη Αρωμάτων & Εξατομίκευση
Φανταστείτε να απαντάτε σε λίγες ερωτήσεις για τις αγαπημένες σας νότες, τις μάρκες ή τις περιστάσεις που αναζητάτε άρωμα και να λαμβάνετε προσωποποιημένες προτάσεις μέσα από χιλιάδες επιλογές. Αυτή είναι η δύναμη του fragrance matching βάσει δεδομένων. Ιδιαίτερα χρήσιμο όταν δοκιμάζετε άγνωστες κατηγορίες αρωμάτων – από φωτεινά κιτρώδη ως πλούσιες ξυλώδεις amber νότες. Οι αλγόριθμοι διαβάζουν τα patterns για να προβλέψουν τι θα σας ταιριάξει.
Η παραδοσιακή ανακάλυψη βασίζεται στην αφηγηματική δύναμη. Ένας ικανός πωλητής ή ένα brand μπορεί να σας ρωτήσει ποιες αναμνήσεις ή διαθέσεις θέλετε να προκαλέσετε – π.χ. έναν ζεστό χειμωνιάτικο βράδυ στη Νέα Υόρκη ή μια ανάλαφρη εκδρομή στην Καλιφόρνια – και να προτείνει αρώματα που συμφωνούν με αυτά τα συναισθήματα.
Ενώ η AI στηρίζεται στην αγοραστική σας ιστορία για να περιορίσει τις ακριβές «αποτυχίες», οι παραδοσιακές μέθοδοι εμπνέουν πιο τολμηρές επιλογές μέσω storytelling. Σήμερα οι περισσότεροι Αμερικανοί αγοραστές συνδυάζουν και τις δύο μεθόδους: ξεκινούν με AI-διαγνωστικά quiz, ύστερα δοκιμάζουν φυσικά δείγματα – όπως strips, decants ή mini vials – για να δουν πώς «κάθεται» το άρωμα στο δέρμα τους. Αυτό το πάντρεμα ακρίβειας και αφήγησης ενισχύει την προσωπική εμπειρία, οδηγώντας τους καταναλωτές σε πλατφόρμες που συνδυάζουν ιδανικά data insights και ανθρώπινη προσέγγιση.
Ο Ρόλος των Πλατφορμών Ανακάλυψης
Η αγορά αρωμάτων έχει εκτοξευθεί – από περίπου 300 λανσαρίσματα το χρόνο τη δεκαετία του ’90, πλέον ξεπερνούν τις 3.000 ετησίως. Αυτή η ποσότητα καθιστά ανέφικτη τη δοκιμή αποκλειστικά με full-size αγορά. Οι πλατφόρμες ανακάλυψης λύνουν το πρόβλημα, προσφέροντας επιλεγμένες μικρές φόρμες και σας επιτρέπουν να ζήσετε με το άρωμα πριν την ακριβή επένδυση σε πλήρες μπουκάλι.
Παράδειγμα το Scento. Διαθέτει decants σε 0.75 ml, 2 ml, 8 ml και προαιρετική συνδρομή 8 ml ανά άρωμα. Έτσι, η αγορά ολοκληρωμένου μπουκαλιού μετατρέπεται σε καλά μελετημένη και ενημερωμένη επιλογή – αποφεύγοντας δαπάνες €200–€300 για άρωμα που μπορεί να μείνει αχρησιμοποίητο.
Όπως παρατήρησε ικανοποιημένη πελάτισσα, η Elena R.: «Αγόραζα πάντα full bottles και μετά το μετάνιωνα – τώρα δοκιμάζω πρώτα, και “βγαίνω” με το άρωμα πριν το “παντρευτώ”.»
Πλοήγηση σε μια Διαρκώς Διευρυμένη Αγορά
Οι πλατφόρμες ανακάλυψης δεν απλοποιούν μόνο την επιλογή – σας βοηθούν να κινηθείτε σε μια συνεχώς διογκούμενη αγορά. Με την AI να επιταχύνει την ανάπτυξη αρωμάτων και τα niche brands να πολλαπλασιάζονται, ο όγκος κυκλοφοριών γίνεται δυσβάσταχτος. Τα curated sample sets, οργανωμένα σε θεματικές – όπως μοντέρνα ambers, AI-δημιουργημένα florals ή γαλλικά chypres – σας επιτρέπουν να συγκρίνετε συγγενικά αρώματα αντί να… σκρολάρετε ατελείωτα.
Πλατφόρμες όπως το Scento, που διαθέτει πάνω από 900 luxury αρώματα από 1.000+ designer και niche brands, επιστρατεύει AI για μηνιαίες επιλογές με βάση τις προηγούμενες σας δοκιμές και αξιολογήσεις. Στη συνέχεια οι curators τις βελτιώνουν, λαμβάνοντας υπόψη εποχικότητα και storytelling.
Αυτό το υβριδικό μοντέλο σας επιτρέπει να διατηρείτε μια βασική συλλογή κλασικών επιλογών αφιερώνοντας παράλληλα budget σε πειραματικά ή AI-δημιουργημένα αρώματα. Παρακολουθώντας τη χρήση σας μέσω app ή spreadsheet, μετατρέπετε την «υπερφόρτωση» προσφορών σε εμπειρία μάθησης. Θα καταλάβετε αν προτιμάτε την ακρίβεια των αλγορίθμων, την τέχνη της παράδοσης ή έναν συνδυασμό τους. Και με το Scento να ετοιμάζει full bottles 30ml+, σύντομα θα μπορείτε να αναβαθμίσετε τα decants σας βάσει πραγματικής χρήσης αντί για αυθόρμητες αγορές. Αυτή η σοφιστικέ ένωση τεχνολογίας και παράδοσης σας προσφέρει τη δύναμη να εξερευνήσετε, να πειραματιστείτε και να καλλιεργήσετε τη συλλογή αρωμάτων σας με αυτοπεποίθηση.
AI-Δημιουργημένα Αρώματα: Το Μέλλον της Αρωματοποιίας;
Συμπεράσματα
Η τεχνητή νοημοσύνη και η παραδοσιακή αρωματοποιία μεταμορφώνουν τον τρόπο που γεννιούνται τα αρώματα, παντρεύοντας τα καλύτερα και των δύο κόσμων. Ενώ οι παραδοσιακές μέθοδοι εμφυσούν στα αρώματα ανθρώπινη διαίσθηση, συναισθηματική αφήγηση και πλούσια ιστορία, η AI προσφέρει ανεπανάληπτη ταχύτητα, ακρίβεια δεδομένων και πρακτικές για περισσότερη βιωσιμότητα. Μαζί, ανοίγουν νέους ορίζοντες στη διερεύνηση μοριακών συνδυασμών με τρόπους που κάποτε έμοιαζαν αδιανόητοι.
Το μέλλον της αρωματοποιίας φαίνεται να στηρίζεται σε υβριδικές ροές εργασίας. Η AI αναλαμβάνει καθήκοντα όπως πρόγνωση τοξικότητας, υπολογισμό παραγωγής άνθρακα και προτάσεις eco-friendly μορίων. Οι αρωματοποιοί εστιάζουν στη βελτίωση της καλλιτεχνικής και συναισθηματικής διάστασης. Προηγμένα εργαλεία επιτρέπουν σε αρωματοποιούς να επιλέγουν υλικά σε οθόνη αφής, με ρομποτικά συστήματα να συνθέτουν ιδανικές φόρμουλες σε λίγες ώρες. Η συνεργασία αυτή εξασφαλίζει καλλιτεχνική ελευθερία διατηρώντας το artisanal άγγιγμα που χαρίζει “ψυχή” στο άρωμα.
Για τους φίλους των αρωμάτων, η σύμπραξη αυτή σημαίνει πιο πλούσια και εξατομικευμένη εμπειρία. Εργαλεία AI προτείνουν αρώματα με εντυπωσιακή ακρίβεια 95%, ενώ επιλεγμένες πλατφόρμες sampling προσφέρουν τη δυνατότητα να ανακαλύψετε τόσο πρωτοποριακές δημιουργίες, όσο και διαχρονικά classics, πριν δεσμευτείτε με πλήρες μπουκάλι. Σε ευρύτερο επίπεδο, αυτή η προσέγγιση μειώνει την ανάγκη για πειράματα σε ζώα και βοηθά τις μάρκες να προβλέπουν καλύτερα τις περιβαλλοντικές τους επιπτώσεις.
Καθώς η παγκόσμια αγορά αρωμάτων αναμένεται να φτάσει τα $69,25 δισ. έως το 2030, οι μάρκες που θα αντιμετωπίσουν την AI ως συνεργάτη και όχι αντικαταστάτη θα θριαμβεύσουν. Το επάγγελμα του αρωματοποιού εξελίσσεται· συγχωνεύει τεχνολογία, δεδομένα και δημιουργικότητα για να φέρει αρώματα που ισορροπούν την αποδοτικότητα με το συναίσθημα. Είτε σας συναρπάζει η ακρίβεια της AI είτε η διαχρονική τέχνη των παραδοσιακών πρακτικών, ο διαρκώς διευρυνόμενος κόσμος των αρωμάτων προσφέρει πλέον κάτι ξεχωριστό για τον καθένα. Αυτή η αρμονική ένωση καινοτομίας και παράδοσης χαρακτηρίζει τη συναρπαστική εξέλιξη της σύγχρονης αρωματοποιίας που διερευνήσαμε εδώ.
Συχνές Ερωτήσεις
Πώς κάνει η AI τη δημιουργία αρωμάτων ταχύτερη και πιο αποδοτική;
Η AI εισάγει νέα διάσταση ταχύτητας και ακρίβειας στη δημιουργία αρωμάτων επεξεργαζόμενη τεράστιες ποσότητες δεδομένων σχετικά με συνδυασμούς νοτών, καταναλωτικές προτιμήσεις και τάσεις της αγοράς. Αυτή η τεχνολογία επιτρέπει την ταχεία ανάπτυξη ξεχωριστών φόρμουλων μειώνοντας δραστικά το χρόνο και το κόστος σε σχέση με τις παραδοσιακές μεθόδους.
Με τη βοήθεια AI, οι αρωματοποιοί μπορούν να εξερευνήσουν ένα τεράστιο εύρος παραλλαγών πολύ πιο γρήγορα από ό,τι με χειροκίνητη δοκιμή. Έτσι, εκτός από εξοικονόμηση χρόνου, διασφαλίζεται πως το τελικό προϊόν ισορροπεί τη δημιουργικότητα με απόλυτη ακρίβεια.
Πώς ωφελεί η AI το περιβάλλον στον κλάδο της αρωματοποιίας;
Η AI στην αρωματοποιία φέρνει σημαντικά οφέλη στη μείωση των αποβλήτων και τη βέλτιστη διαχείριση των πόρων. Η ακριβής διαμόρφωση ελαχιστοποιεί την ανάγκη για περίσσεια πρώτων υλών και περιορίζει ουσιαστικά τα χημικά απόβλητα. Επιπλέον, η AI απλοποιεί τις διαδικασίες παραγωγής και τις εφοδιαστικές αλυσίδες, μειώνοντας τη συνολική ενεργειακή κατανάλωση και το αποτύπωμα άνθρακα του κλάδου.
Χάρη στην αποδοτικότητα που προσδίδει η AI στη δημιουργία αρωμάτων, η βιομηχανία μπορεί να περιορίσει την υπερπαραγωγή και να ελαχιστοποιήσει το οικολογικό της αποτύπωμα σε σύγκριση με τις συμβατικές μεθόδους.
Μπορεί η AI να δημιουργήσει αρώματα με το ίδιο συναισθηματικό βάθος όπως η παραδοσιακή αρωματοποιία;
Η AI διευρύνει τους ορίζοντες στην εξατομικευμένη δημιουργία αρωμάτων, αξιοποιώντας δεδομένα για να «αγγίξει» προσωπικές προτιμήσεις με τρόπους που δεν ήταν δυνατοί στο παρελθόν. Εισάγει μια φρέσκια, τεχνολογικά καθοδηγούμενη προσέγγιση, ανοίγοντας νέες ευκαιρίες για καινοτομία.
Ωστόσο, η παραδοσιακή αρωματοποιία είναι ένας κόσμος βαθιά ριζωμένος στην ανθρώπινη τέχνη, αφήγηση και κληρονομιά – στοιχεία που συγκινούν σε συναισθηματικό επίπεδο. Η δεξιοτεχνία και η διαίσθηση που καλλιεργούνται μέσα από χρόνια εμπειρίας οδηγούν σε αρώματα που αφηγούνται ιστορίες και ξυπνούν μνήμες με τρόπους που η τεχνολογία ακόμα δεν μπορεί να προσεγγίσει.
Αν και η AI αποτελεί ισχυρό εργαλείο ενίσχυσης και επέκτασης των παραδοσιακών τεχνικών, δεν μπορεί να συλλάβει το περίπλοκο συναισθηματικό βάθος και τις δημιουργικές αποχρώσεις που μόνο το ανθρώπινο χέρι και πάθος μπορούν να αποδώσουν στην τέχνη της αρωματοποιίας.






